
Table of Contents
Introduction:
Solid State Drives (SSDs) have changed the world of computing with their data transfer speeds. Unlike traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), SSDs use flash memory to store data, eliminating mechanical components and reducing access times significantly; hence, SSDs performance, speed, and reliability are way higher than HDDs. SSDs are most popular among gamers because of their low loading times. Many users wonder how many SSD can a pc have.
How many SSD can a pc have ?
Its depends on the motherboard support. Check your Motherboard manual and look for number of SATA, M.2, PCIe ports, the more you have these ports the more SSDs you can attach with the computer.
Understanding SSDs and Their Advantages:
The advantages include lightning-fast boot times, quicker application loading, energy efficiency, silent seamless multitasking. The absence of moving parts in SSDs leads to improved durability and reduced risk of data loss due to physical damage, making them ideal for any purpose.
Factors Affecting the Number of SSDs a PC Can Have:
A. Motherboard Compatibility:
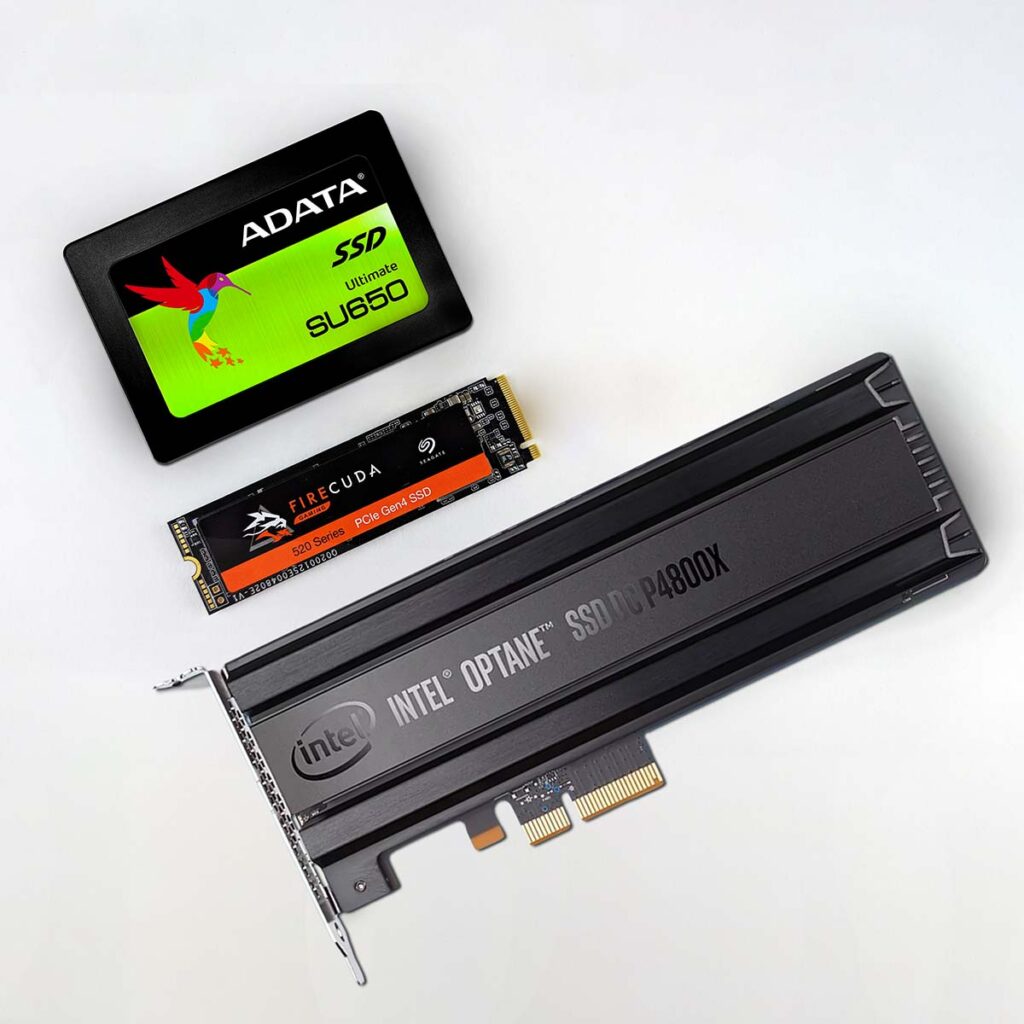
Types of SSD interfaces: PCs support different SSD interface types, including SATA, M.2, and PCIe. SATA is commonly found in older systems, while M.2 and PCIe provide faster speeds and are featured in modern motherboards.
Number of available PCIe lanes and M.2 slots: The number of PCIe lanes and M.2 slots on a motherboard determines how many SSDs it can support. High-end motherboards often offer more slots, allowing for multiple SSDs.
B. Form Factor and Physical Space:
Standard 2.5-inch SSDs: These are the most common SSDs and can be easily installed in most desktops and laptops that have 2.5-inch drive bays.
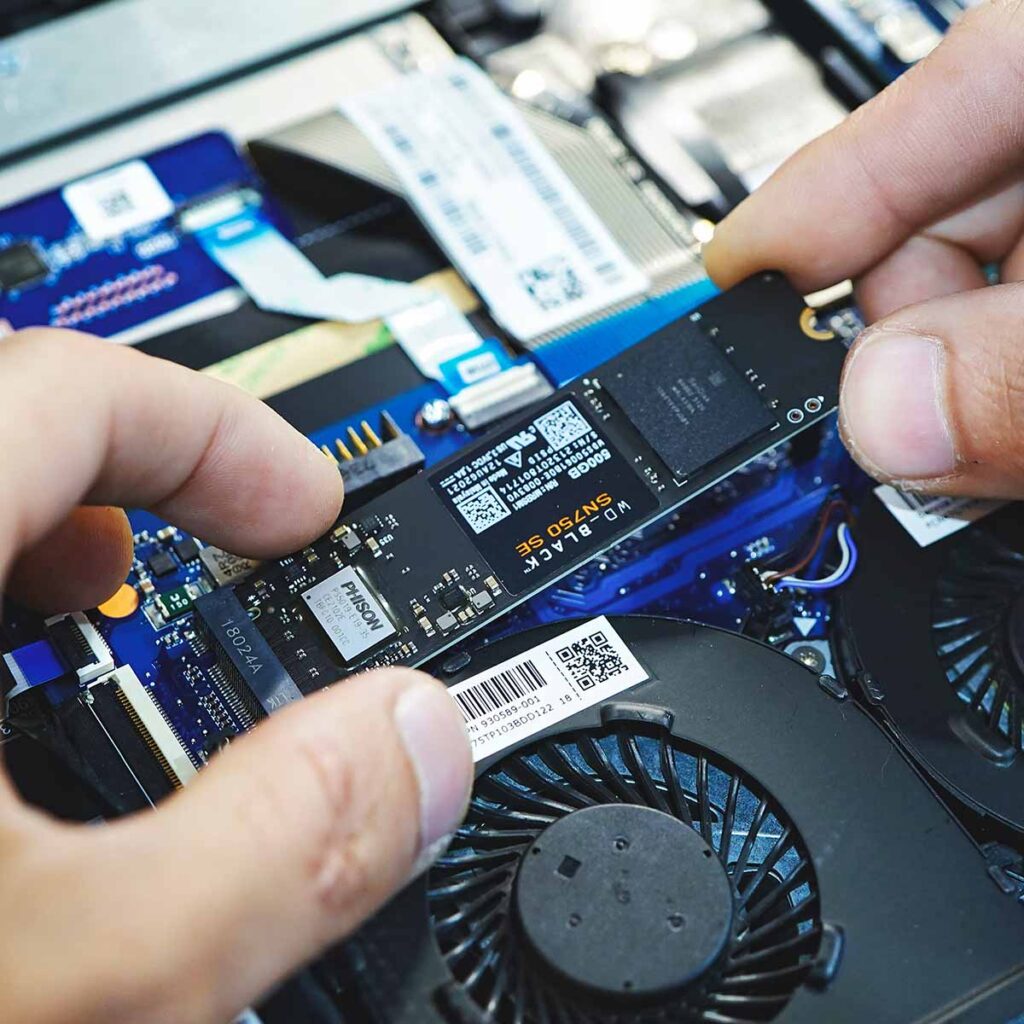
Compact M.2 SSDs: M.2 SSDs are smaller and directly attach to the motherboard, requiring less physical space and providing a clutter-free design. Different lengths of M.2 SSDs (Type 2242, 2260, 2280) are available, so ensure your motherboard supports the specific length you choose.
C. Power and Cooling Considerations:
Power supply capacity and connectors: Multiple SSDs can increase power demands, so it’s essential to have an adequate power supply and the necessary connectors to power them.
Potential overheating issues: SSDs generate heat during operation, especially under heavy loads. Ensuring proper airflow and using SSD heatsinks can prevent overheating.
Common Scenarios for SSD Configurations:
The number of SSDs you can install in your PC depends on your needs and budget. Here are some common configurations:
A. Entry-Level PC Setup:
Single SSD installation: For basic computing needs, a single SSD with sufficient storage capacity can provide a significant performance boost over an HDD.
B. Mid-Range PC Setup:
Combining SSD and HDD: Many users opt for a combination of SSD and HDD, using the SSD for the operating system and frequently accessed applications, and the HDD for bulk storage.
Dual SSD configuration: With mid-range PCs, users can install two SSDs, one for the OS and applications and the other for additional storage or specific tasks.
C. High-End PC Setup:
Multiple SSDs in RAID configurations: High-end PC users often employ RAID arrays, which combine multiple SSDs for increased speed and data redundancy. RAID 0 enhances speed, while RAID 1 provides data mirroring for redundancy.
Utilizing PCIe Gen4: The latest PCIe Gen4 interface offers unprecedented speeds, making it ideal for high-performance PCs that demand rapid data transfer.
Challenges and Limitations:
While SSDs offer numerous advantages, there are some challenges and limitations to consider:
A. Cost considerations: SSDs can be more expensive than traditional HDDs, especially when opting for high-capacity models or multiple drives.
B. Space constraints: Smaller form factor PCs may have limited physical space for multiple SSDs, requiring careful planning and selection of suitable components.
C. Compatibility issues: Older PCs might have limited support for newer SSD types or lack the necessary interfaces, limiting the number of SSDs you can install.
Conclusion:
SSDs have become an essential component in a PC due to their superior speed, reliability, and power efficiency. The number of SSDs a PC can have depends on motherboard compatibility, physical space, power supply capacity, and cooling solutions. Although a single SSD is often sufficient, mid-range and high-end PC setups can benefit from multiple SSD configurations. Regardless of the configuration, regular data backups remain crucial for safeguarding data.
FAQ Section:
A. Can I mix different types of SSDs in my PC?
Yes, you can mix different types of SSDs, such as SATA SSDs with M.2 or PCIe SSDs. It depends on your needs. However, ensure that your motherboard supports the specific interfaces you plan to use.
B. How do I check the number of available PCIe lanes on my motherboard?
You can find the number of available PCIe lanes in your motherboard’s specifications or user manual. Additionally, modern BIOS/UEFI interfaces often provide this information.
C. Can I use an external SSD in addition to internal SSDs?
Yes, you can use external SSDs via USB or Thunderbolt ports, they are handy and portable and you can find plenty of option and different sizes and shapes available in the market.
D. What is RAID, and is it beneficial for SSDs?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) combines multiple drives to improve performance, data redundancy, or both. RAID can benefit SSDs by increasing speed through RAID 0 or providing data redundancy with RAID 1.
E. Are there any compatibility issues with using SSDs in older PCs?
Yes, older PCs might lack support for newer SSD interfaces like M.2 or PCIe Gen4. Additionally, some older motherboards may not be optimized for SSD usage like motherboard doesn’t support 6Gbps transfer speeds, leading to suboptimal performance. Always check your PC’s specifications and compatibility before upgrading to SSDs.






